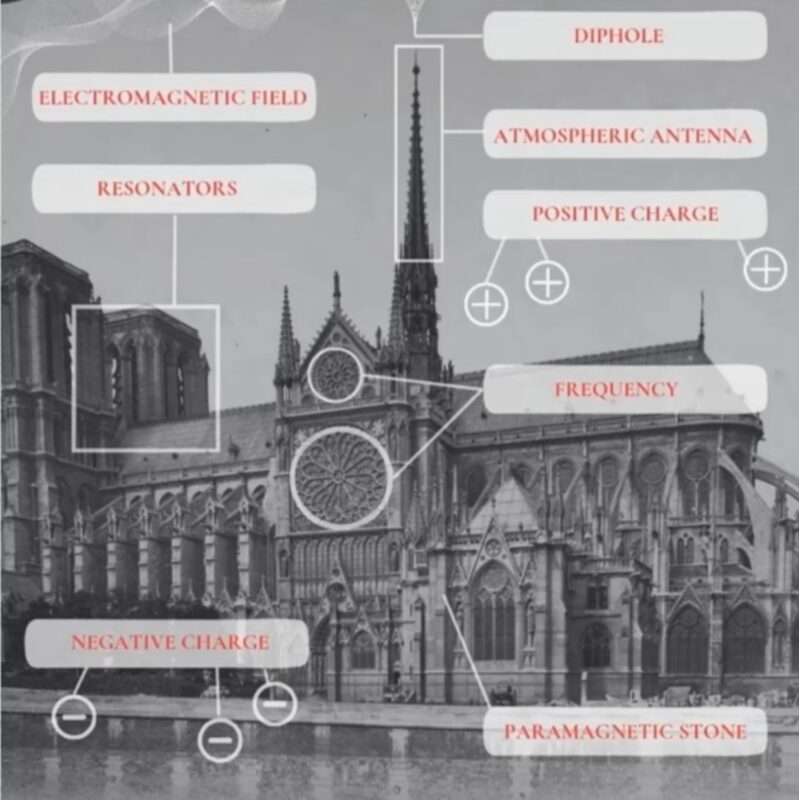
For centuries, whispers of ancient civilizations harnessing free energy have circulated. Structures like pyramids and temples, incorporating elements like dipholes, resonators, and paramagnetic stones, hint at technologies far beyond our current understanding. While the exact mechanisms remain shrouded in mystery, these historical clues spark a fascinating inquiry: could we replicate—or even surpass—these ancient feats by tapping into the vast, untapped energy potential of the atmosphere and water?
The concept hinges on understanding the Earth’s natural electromagnetic field. This field, a dynamic interplay of positive and negative charges, permeates everything. Ancient builders may have intuitively understood how to leverage this field, using structures acting as atmospheric antennas to capture and amplify its energy. The dipholes, for example, might have served as conduits, channeling the electromagnetic flow. Resonators, strategically placed within these structures, could have amplified specific frequencies within the electromagnetic field, creating a resonant effect that generated usable energy. Paramagnetic stones, with their unique magnetic properties, may have played a crucial role in this process, potentially acting as energy conductors or amplifiers.
Modern science offers potential explanations for how such a system might function. The atmosphere itself is a vast reservoir of electrical energy, constantly being generated by solar radiation and atmospheric processes. This energy manifests as electromagnetic waves spanning a wide range of frequencies. By carefully designing structures that act as efficient atmospheric antennas, we could potentially capture and convert this ambient energy into usable power. The key lies in understanding the resonant frequencies of the Earth’s electromagnetic field and designing structures that effectively capture and amplify these frequencies.
Water, too, presents a compelling avenue for free energy exploration. Water molecules possess a unique dipole moment, meaning they have a positive and negative end. This inherent polarity makes water highly susceptible to electromagnetic influences. By applying specific frequencies to water, we might be able to induce oscillations and generate energy. Furthermore, the movement of water itself—waves, currents, tides—represents a significant kinetic energy source that could be harnessed.
However, significant challenges remain. The energy density in the atmosphere and water is relatively low, requiring highly efficient energy harvesting technologies. Understanding the precise resonant frequencies and optimizing antenna design are crucial steps. Furthermore, the environmental impact of large-scale energy harvesting from these sources needs careful consideration.
Despite these challenges, the potential rewards are immense. Harnessing free energy from the atmosphere and water could revolutionize our energy infrastructure, providing a clean, sustainable, and virtually limitless power source. Further research into the principles underlying ancient energy technologies, combined with modern scientific advancements in materials science, electromagnetism, and fluid dynamics, could unlock a new era of energy independence and environmental sustainability. The whispers of the past may yet guide us to a brighter, more energy-secure future.